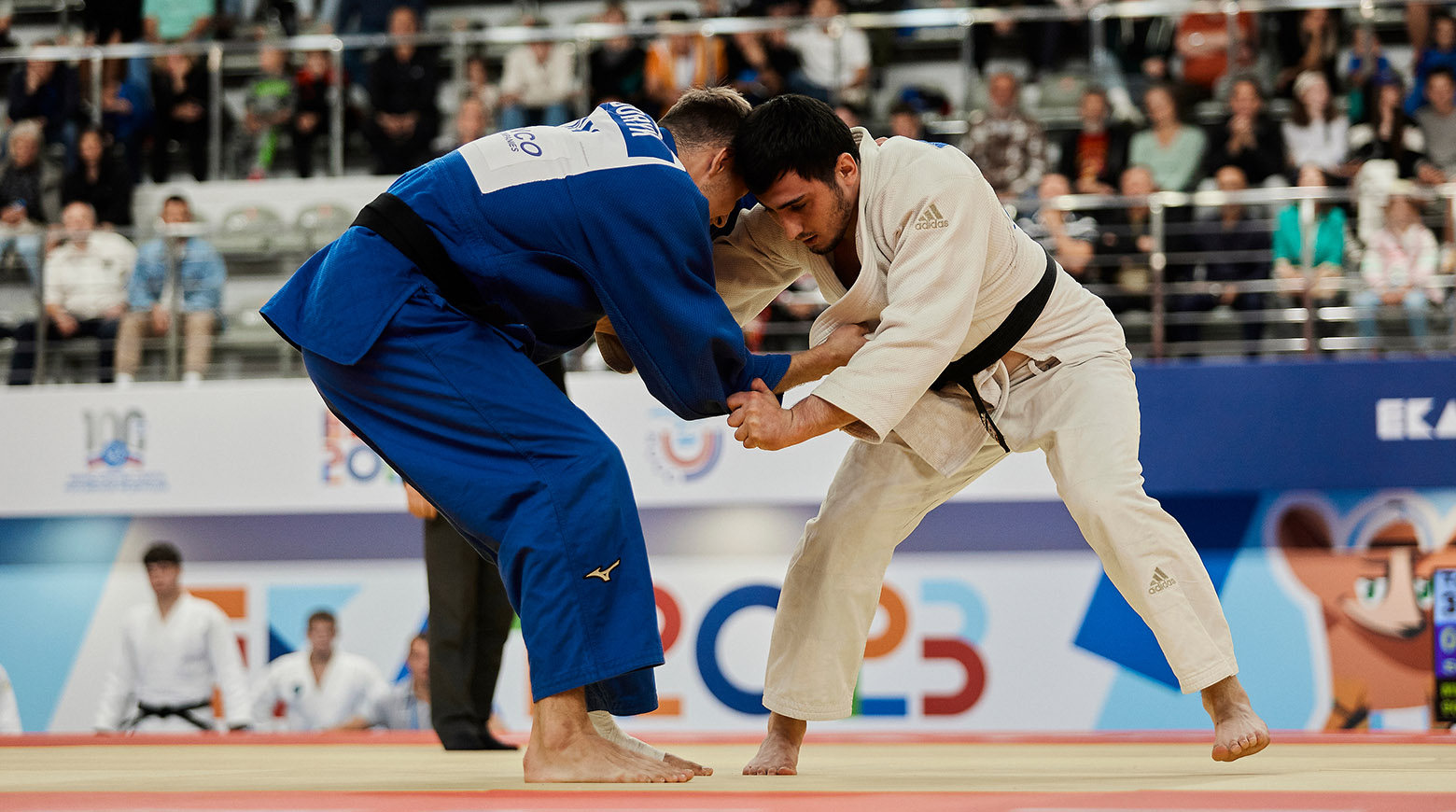
Judo
Judo is a type of martial art whose technique is based on throws, painful arm holds, submissions and chokes.
Disciplines

History
Judo was founded by the martial artist Jigoro Kano. In 1882, Kano founded a judo school called Kodokan in Japan, creating a wrestling system and principles of mental and physical training. The name "judo" translates as "flexible way".
The first men's world judo championship was held in Tokyo in 1956, and in 1964 judo was added to the Olympic programme in the Japanese capital. The first women's world championship was held in 1980, and judokas have competed in the Olympic Games since 1992.
The first judo school in Russia was opened in 1914 in Vladivostok by Vasily Oshchepkov, a Kodokan graduate. The USSR Judo Federation was founded in 1972. The first Olympic gold medal for the USSR was won by Shota Chochishvili at the Munich Games in 1972, and the first Soviet world champion was Vladimir Nevzorov in Vienna in 1975. Subsequently, Soviet wrestlers climbed to the top of the Olympic and world podiums more than once. In 1980, a judo tournament was held as part of the XX Summer Olympics in Moscow, and in 1983, the capital of the USSR hosted the World Championships for the first time in history.
Rules
An Ippon is the highest score in judo. It is awarded for a clean victory, which is achieved through a rapid and forceful throw that is conducted with total control. The throw must cause the opponent to land largely on their back or in the bridge position (touching the mat with their head and one or both legs at the same time). If the throw does not meet the requirements for an Ippon, a Waza-ari is awarded. This can occur when the opponent falls backwards on his side, on his buttocks and arms or elbows, or rolls over on his shoulder blades or lower back. No awards are made if the opponent falls on their stomach or falls forwards on their side.
In the prone position, a contestant can earn an Ippon by successfully maintaining a joint lock or choke until the opponent surrenders by saying 'maitta' or tapping on the mat/opponent twice or more with their hand. Alternatively, an Ippon can be awarded for holding the opponent down on their back for 20 seconds. A Waza-ari is awarded for holding the opponent down for 10 to 19 seconds. Two Waza-aris result in an Ippon, meaning a contestant with two Waza-aris wins the fight.
If a contestant violates minor judo rules, such as excessive passivity, using unconventional holds that result in a negative style of fighting, or deliberately leaving the competition area, a penalty (Shido) will be given to the contestant. If a contestant receives three Shidos, they will lose the fight. For serious violations, such as actions that endanger the health of the contestant or their opponent, or actions that go against the spirit and ethics of judo, the contestant will receive a reprimand (Hansoku-make) and will be disqualified from the fight and, in most cases, from the competition.
Top Three Facts
Judo is the world's most popular martial art and one of the most popular sports in terms of fans. Judo is practised by around 30 million people worldwide.
Yasuhiro Yamashita (Japan) is the only judoka in the world to leave the sport undefeated. He has 217 official fights to his credit and not a single defeat.
The International Judo Federation is now one of the three most representative sports organisations in the world - with more than 200 national federations from every continent except Antarctica.